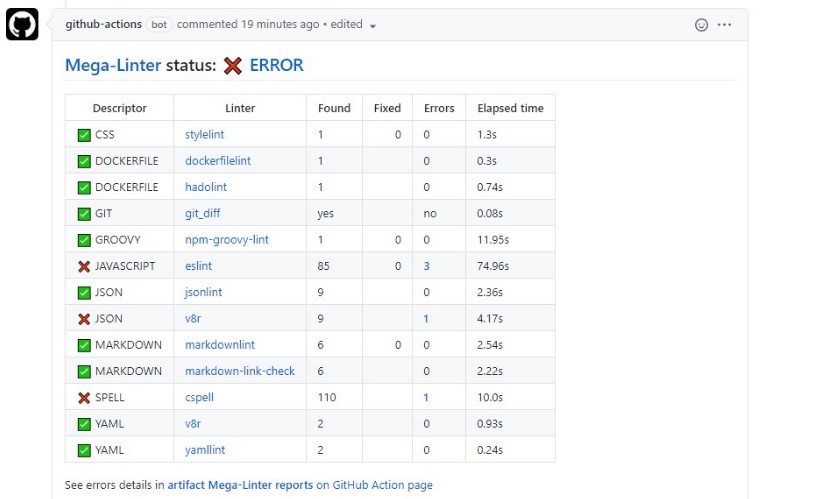
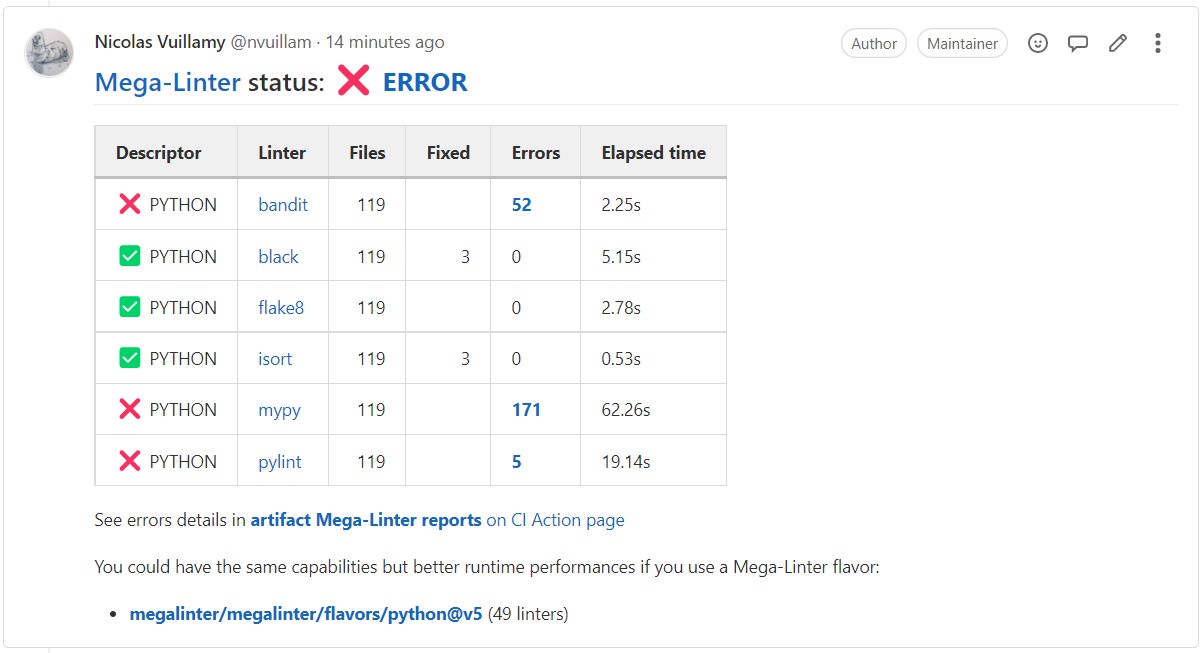
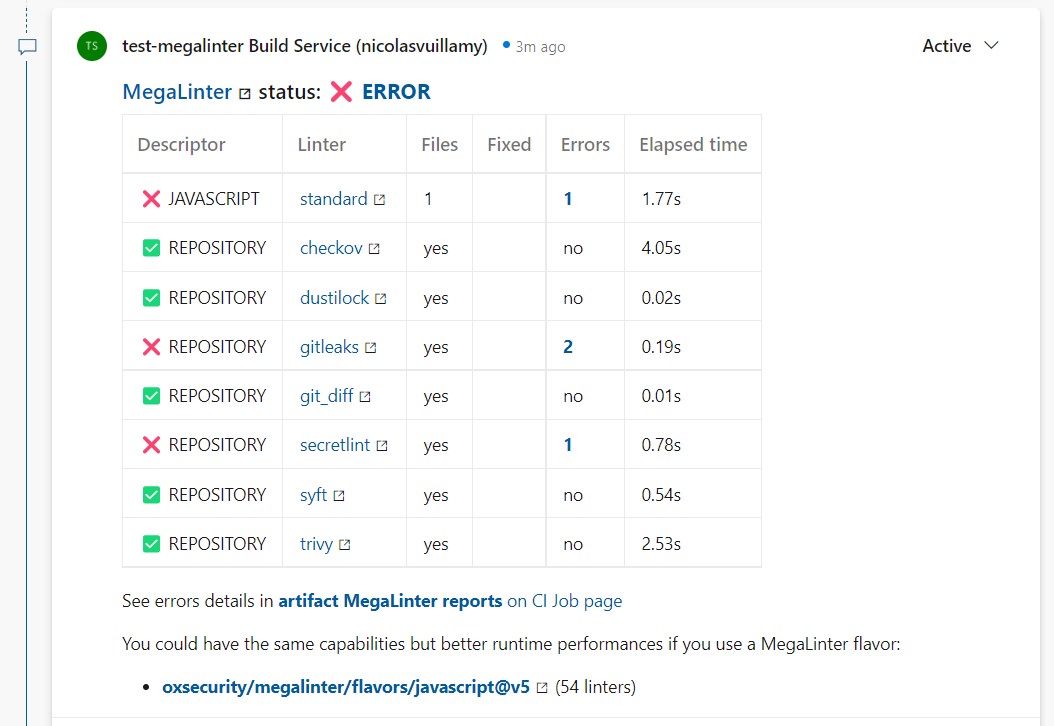
MegaLinter vs Super-Linter
The hard fork of Super-Linter to Python isn't just a language switch: Python's flexibility and libraries enabled many additional features described below.
Security
MegaLinter hides many environment variables when calling the linters.
That way you need to trust only MegaLinter core code with your secrets, not the 100+ embedded linters !
Performance
- MegaLinter flavors allow using smaller Docker images, reducing pull time.
- Thanks to Python multiprocessing, linters are run in parallel, which is much faster than Super-Linter's Bash script that runs all linters sequentially.
- When the linter allows it, call it once with N files, instead of calling it N times with one file.
More languages and formats linted
- C, C++, Copy-Paste detection, Credentials, GraphQL, JSON & YAML with JSON schemas, Markdown tables formatting, Puppet, reStructuredText, Rust, Scala, Spell checker, Swift, Visual Basic .NET …
Automatically apply formatting and fixes
MegaLinter can automatically apply fixes performed by linters and push them to the same branch, or create a Pull Request that you can validate.
This is pretty handy, especially for linter errors related to formatting (in that case, you don't have any manual update to perform)
Run locally
MegaLinter can be run locally thanks to mega-linter-runner.
Reports
Capabilities
- Accuracy: Count the total number of errors, not only the number of files in error.
- Show linter version and applied filters for each linter processed.
- Reports stored as artifacts on GitHub Actions runs or other remote files
- General log
- One report file by linter
Additional Reporters
Enhanced configuration
- Assisted installation and configuration using a Yeoman generator and JSON schemas for the configuration file
- Configure include and exclude regexes for a single language or linter: e.g.,
JAVASCRIPT_FILTER_REGEX_INCLUDE (src) - Configure additional CLI arguments for a linter: e.g.,
JAVASCRIPT_ES_ARGUMENTS "--debug --env-info" - Configure non-blocking errors for a single language or linter: e.g.,
JAVASCRIPT_DISABLE_ERRORS - Simplified languages and linters variables
- ENABLE = list of languages and formats to apply lint on codebase (default: all)
- ENABLE_LINTERS = list of linters to apply lint on codebase (default: all)
- DISABLE = list of languages and formats to skip (default: none)
- DISABLE_LINTERS = list of linters to skip (default: none)
- Variables VALIDATE_XXX are still taken in account (but should not be used in association with ENABLE and DISABLE variables)
Enhanced documentation
- One page per linter documentation:
- All variables that can be used with this linter
- List of file extensions, names and filters applied by the linter
- Link to MegaLinter default linter configuration
- Link to linter website
- Link to official page explaining how to customize the linter rules
- Link to official page explaining how to disable rules from source comments
- Examples of linter command line calls behind the hood
- Help command text
- Installation commands
- Installation links for related IDEs
- README
- Separate languages, formats, and tooling formats in the linters table
- Add logos for each descriptor
Plugin management
For less commonly used linters, MegaLinter offers a plugin architecture so anyone can publish plugins.
Simplify architecture and evolutionary maintenance
- Refactoring runtime in Python, for easier handling than Bash thanks to classes and Python modules
- Everything related to each linter is in a single descriptor YAML file
- Easier ongoing maintenance
- Fewer conflicts to manage between PRs
- A few special cases require a Python linter class)
- Default behaviors for all linters, with the possibility to override parts of them for special cases
- Hierarchical architecture: Apply fixes and new behaviors to all linters with a single code update
- Documentation as code
- Generate linters tables (ordered by type: language, format, and tooling format) and include them in the README. (see result)
- Generate one markdown file per linter, containing all configuration variables, information, and examples (see examples)
- Automatic generation of Dockerfiles using YAML descriptors, always using the linter's latest version
- Dockerfile commands (FROM, ARG, ENV, COPY, RUN)
- APK packages (Linux)
- NPM packages (Node.js)
- PIP packages (Python)
- GEM packages (Ruby)
- Phive packages (PHP)
- Have a centralized exclude list (node_modules, .rbenv, etc.)
Improve robustness & stability
- Test classes for each capability
- Test classes for each linter: automatic generation of test classes using .automation/build.py
- Set up code coverage
- Development CI/CD
- Validate multi-status on PR inside each PR (posted from step "Run against all code base")
- Run test classes and code coverage with pytest during validation GitHub Action
- Validate descriptor YML files with json schema during build
- Automated job to upgrade linters to their latest stable version